
Are you putting the same effort into your sleep routine as your workouts? If not, you might be missing out on a huge piece of the fitness puzzle!
Sleep isn’t just about recharging your batteries—it’s the secret sauce that helps you recover faster, keep your hormones in check and build muscle,
In this guide, we’ll dive into why sleep is so crucial for your health and fitness, plus the science-y stuff like how sleep hormones (hello, human growth hormone!) affect everything from your gains to your cravings.
The Science of Sleep – Breaking Down the Sleep Cycle
You’ve probably heard that getting enough sleep is crucial, but what’s really happening while you’re catching those Zzz’s?
Sleep isn’t just one long, dreamy stretch—it’s actually broken down into different stages, each playing its own role in helping you recover, repair, and recharge. Let’s break it down.
The Stages of Sleep
Your body goes through cycles of sleep every night, typically cycling through 4-5 times, with each cycle lasting about 90 minutes. Each stage has a unique function that’s essential for both your overall health and fitness performance.
Non-REM Sleep:
REM stands for Rapid Eye Movement
This stage is where the real magic happens when it comes to physical recovery.
Stage 1: This is light sleep, the bridge between wakefulness and sleep. It’s the "dozing off" period when your body starts to relax.
Stage 2: A deeper state of relaxation kicks in here. Your body temperature drops, your heart rate slows, and your muscles relax, all preparing you for deep sleep.
Stage 3 (Deep Sleep): This is the deep, restorative sleep where muscle repair, growth, and immune function thrive. Your body produces Human Growth Hormone (HGH) during this stage, making it vital for anyone serious about fitness and recovery. The more deep sleep you get, the better your muscles recover from those tough workouts!
REM Sleep:
Ever had those vivid dreams that feel super real? That’s happening in REM sleep. But REM is about more than just dreamland—it’s important for brain health. During this stage, your brain processes and stores information, improving memory and cognitive function.
For fitness enthusiasts, REM sleep helps with motor learning—so those new moves you practiced at the gym or on the field? They’ll stick better after a good night’s REM sleep.
Quality vs. Quantity
You’ve probably heard the rule: “Get 7-9 hours of sleep each night.” But it’s not just about hitting that number. Both quality and quantity of sleep matter. You could be in bed for 8 hours, but if you’re tossing and turning all night, you’re not getting the deep and REM sleep your body needs for recovery.
Sleep Quality: This refers to how much time you spend in the restorative stages (deep and REM) versus light, restless sleep.
Sleep Quantity: The total amount of time you spend sleeping. Without enough hours of sleep, your body doesn’t get a full chance to cycle through these important stages.

Ideal Sleep Duration for Fitness Enthusiasts
Whether you are a fitness enthusiast or not, I always recommend 7-9 hours of sleep per night.
If you’re regularly pushing yourself in the gym or doing intense workouts, your body might need a little extra. I'm sure you've noticed that you tend to sleep better after exercising.
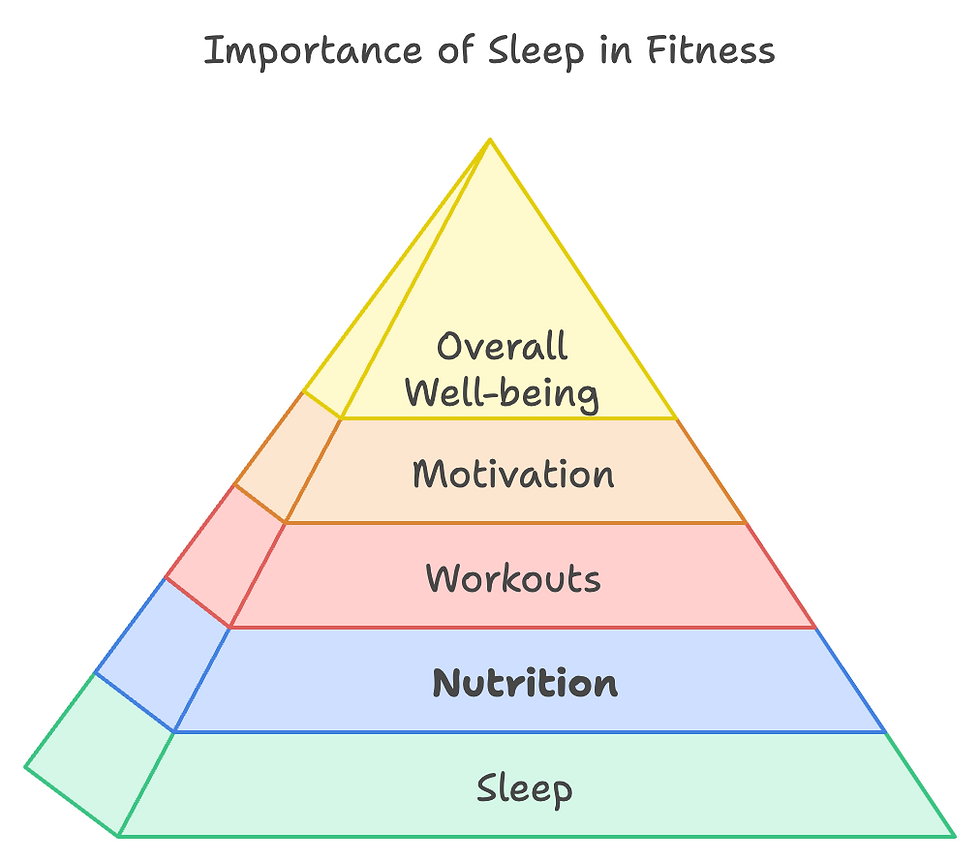
Getting to know the ins and outs of your sleep cycle helps you understand why good sleep is as essential as a balanced diet and effective workout routine.
In the next section, we’ll dive into the hormones that are busy working behind the scenes while you sleep—and how they affect everything from muscle recovery to hunger!
The Hormones of Sleep – Your Body’s Nighttime Superstars
When you think about sleep, you might picture your body completely at rest, doing nothing. But in reality, while you’re snoozing, your body is hard at work, producing and regulating hormones that are critical for both health and fitness.
These sleep hormones don’t just help you rest—they also play a huge role in how you recover, build muscle, manage your hunger, and even maintain a healthy weight. Let’s dive into the key players!
1. Human Growth Hormone (HGH) – The Muscle Builder
HGH is like the body’s natural recovery crew, and it does most of its work while you sleep.
Produced by the pituitary gland, HGH helps repair and build muscle tissue, aids in recovery after tough workouts, and even promotes fat metabolism.
When does it work? During deep sleep (Non-REM Stage 3), your body releases the highest amount of HGH. This is why deep sleep is crucial for athletes and fitness enthusiasts—without enough of it, your body isn’t able to fully recover, and you could be leaving gains on the table.
Why does it matter? If you’re consistently skimping on sleep, your HGH levels decrease, slowing down muscle recovery and growth. This can leave you feeling sore for longer, increase your injury risk, and make it harder to hit your fitness goals.
As a side note, HGH is a very sought after PED (performance enhancing drug) which is banned by the anti- doping agency. I'm saying this to drive home the point that it is so important that people make a lot of money selling it.
2. Cortisol – The Stress Hormone
Cortisol is often misunderstood, but it’s a hormone that’s essential in the right amounts. It helps regulate metabolism, control blood sugar levels, and manage stress.
However, when cortisol levels are too high, it can have negative effects on your fitness and overall health.
When does it work? Cortisol levels naturally decrease during sleep, reaching their lowest point around midnight. As the morning approaches, cortisol starts to rise again, helping to wake you up and get you moving.
Why does it matter? Poor sleep—or not enough sleep—keeps cortisol levels high, which can lead to increased stress, fat storage (especially around the belly), and even muscle breakdown. High cortisol also suppresses the production of HGH, making recovery even tougher.
3. Leptin and Ghrelin – The Hunger Hormones
If you’ve ever had a bad night’s sleep and found yourself craving every carb in sight the next day, you can blame leptin and ghrelin. These two hormones control your appetite and how full you feel.
Leptin: This is the hormone that tells your brain when you’re full. When you get enough quality sleep, leptin levels stay balanced, helping you control cravings and make healthier food choices.
Ghrelin: Often called the “hunger hormone,” ghrelin is responsible for making you feel hungry. After a poor night’s sleep, ghrelin levels spike, making you crave high-calorie, sugary foods.
Why does it matter? Lack of sleep throws off the balance between leptin and ghrelin, causing you to feel hungrier and less satisfied after eating. This can lead to overeating, weight gain, and make it harder to stick to your fitness or weight loss goals.
4. Melatonin – The Sleep Regulator
Melatonin is the hormone that controls your sleep-wake cycle, signalling to your body when it’s time to wind down and get some rest. It’s affected by light exposure, which is why dimming the lights or avoiding screens before bed can help your body produce melatonin more effectively.
When does it work? As it gets darker in the evening, melatonin levels start to rise, helping you feel sleepy. If your body’s natural melatonin production is disrupted (due to stress, artificial light, or irregular sleep schedules), falling asleep becomes more difficult.
Why does it matter? Without proper melatonin production, you’ll struggle to get quality sleep, which affects all the other hormones we’ve just talked about—ultimately slowing your progress and leaving you feeling tired and unmotivated.
So, what’s the takeaway? Your hormones are working hard for you while you sleep, helping you recover, build muscle, and even control your cravings. When sleep is cut short or of poor quality, these hormones can fall out of balance, making it harder to reach your fitness goals.
In the next section, we’ll talk about how a lack of sleep can sabotage your progress and what you can do to fix it!
Section 4: How Poor Sleep Affects Your Fitness Goals
I know, from personal experience, how tempting it is to "power through" crappy sleep. I've done it, I've seen my friends do, and I've seen my clients do it. 5-6 cups of coffee throughout the day does the trick and we can indeed go long periods of time without proper sleep.
But the truth is, poor sleep can seriously mess with your fitness goals, and over all health on the long term. From slower muscle recovery to uncontrollable cravings, lack of quality sleep can sabotage all the hard work you’re putting in at the gym.
Let's break it down.
1. Slower Muscle Recovery and Growth
Remember Human Growth Hormone (HGH) from the last section? It’s released during deep sleep, helping with muscle repair, regeneration, and overall recovery.
How poor sleep affects it: When you don’t get enough deep sleep, your body doesn’t release as much HGH, meaning your muscles can’t recover as quickly or as effectively. This not only leaves you feeling sore for longer but also slows down muscle growth. Over time, you might notice it’s harder to make gains, even if you’re pushing yourself in the gym.
2. Reduced Endurance and Stamina
Lack of sleep directly impacts your energy levels, endurance, and stamina, making it harder to power through your usual sets or cardio sessions.
How poor sleep affects it: When you’re sleep-deprived, your body and brain are working with limited resources. This means your muscles tire out faster, and your overall endurance takes a hit. You might find yourself struggling to lift the weights you normally handle with ease or cutting your workout short because you just don’t have the energy.
3. Increased Risk of Injury
Sleep doesn’t just affect how you feel; it also impacts how well your body functions.
When you’re low on sleep, your coordination, reaction time, and focus can all suffer. This increases the likelihood of making mistakes during your workout—like lifting with poor form or losing balance during exercises—putting you at a higher risk for injury.
This is even more important for those engage in collective sports where there are so much more unknown variables for your body to handle than simply lifting weights at the gym.
4. Weight Gain and Cravings
Sleep is a huge player in managing your metabolism and appetite, and poor sleep is linked to weight gain.
When you’re not getting enough rest, your body’s hunger hormones—leptin and ghrelin—get thrown out of whack. Leptin tells you when you’re full, and ghrelin makes you hungry.
With less sleep, ghrelin levels rise, and leptin levels drop, meaning you’re likely to feel hungrier and less satisfied after meals.
How poor sleep affects it: Cravings for junk food, particularly sugary and high-carb foods, skyrocket when you’re sleep-deprived. Your body craves quick energy sources to make up for the lack of rest, making it harder to stick to healthy eating habits. On top of that, poor sleep disrupts your body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, leading to fat storage—especially around the belly area. So, even if you’re working out consistently, lack of sleep could be causing weight gain or stalling your fat loss.
5. Lower Motivation and Focus
It’s no secret that sleep affects your mood and mental clarity.
If you’re not getting enough rest, motivation can drop, and you might find it harder to stay focused during your workouts. That mental fog makes it more difficult to stay on track, whether it’s sticking to your meal plan, pushing through a tough workout, or even just finding the energy to go to the gym in the first place.
How poor sleep affects it: Poor sleep makes your brain feel foggy and unmotivated, which can make you slack off during workouts or even skip them altogether. It’s harder to push yourself when your body and brain are tired, and you might not even realize it’s sleep—or lack thereof—that’s holding you back.
Sleep is one of the first thing we disregard as we get busy. With the modern grind culture it's even seen as a badge of honour to function on less sleep. It's a badge of sh*t is you ask me.
The detriments of poor sleep far outweighs whatever benefits you think it leads to. Want to grind you way to riches or get a chiseled physique? Get enough sleep and work smarter, not harder.
In the next section, we’ll go over some actionable tips to help you improve your sleep and get back on track toward crushing your fitness goals.
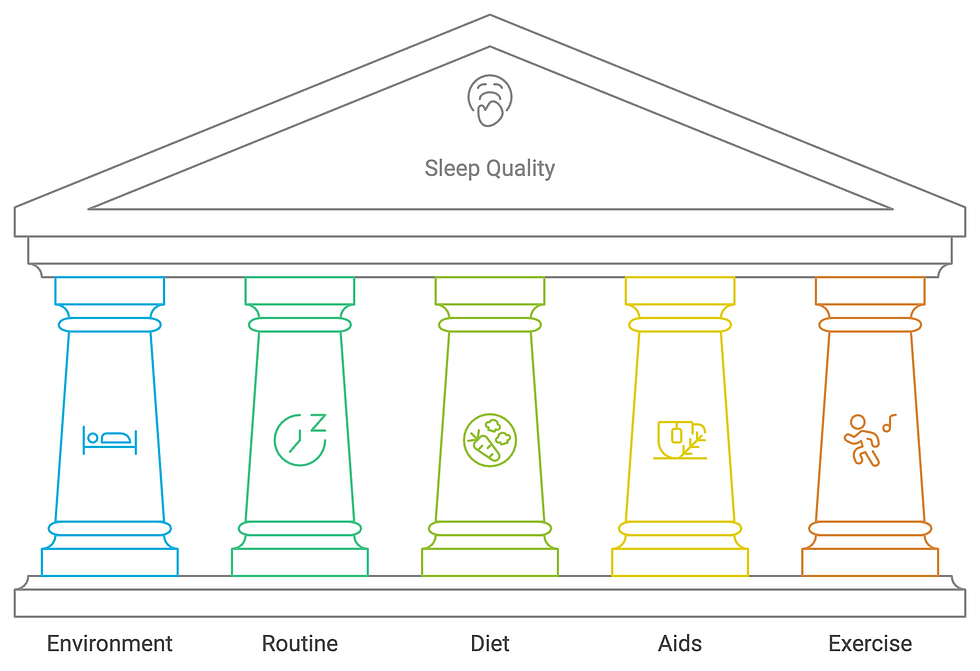
Tips to Improve Sleep for Better Health and Fitness
Now that you know how important sleep is for your fitness goals, it’s time to make sure you’re getting the best quality rest possible.
Improving your sleep doesn’t have to be complicated. With a few simple tweaks to your routine and environment, you can level up your sleep game seamlessly.
1. Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Your bedroom should be a sleep sanctuary. A health heaven. A peaceful, comfortable environment makes a huge difference in how well you sleep.
Keep It Cool: Your body temperature naturally drops when you sleep, so keeping your room slightly cooler can help you drift off faster. Aim for a temperature between 60-67°F (15-19°C).
Block Out Light: Darkness signals your body to produce melatonin, the hormone that helps you fall asleep. Invest in blackout curtains or wear a sleep mask to keep your room as dark as possible.
Limit Noise: If you live in a noisy area or have trouble with distractions, consider using white noise machines or earplugs to block out sounds that could disturb your sleep. Ear plugs have been game changer for me on my travels, especially in cheaper hotels where sound proofing is not a thing apparently.
Upgrade Your Bedding: A comfortable mattress and pillows make all the difference. If you’re waking up sore or uncomfortable, it might be time to invest in quality bedding that supports your body.
Leave your phone outside the bedroom: If you use your phone as an alarm clock, get yourself a normal alarm clock. They're cheap don't worry. If you keep your phone by your bedside table, you will spend time on it before bed. Guaranteed. Don't even try to say otherwise.
2. Develop a Consistent Sleep Routine
Just like you have a workout routine, you need a sleep routine too.
Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up feeling refreshed.
Stick to a Schedule: Aim to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Consistency is key for training your body to sleep well. It's ok to stay in bed after you wake up on weekends, if you enjoy doing so. I do it, I'm writing this article from bed right now. What we don't want is to wake up at wildly different times throughout the week. That's why working shifts is so hard.
Wind Down Before Bed: Give yourself at least an hour of “wind-down” time before bed to relax and signal to your body that it’s time to sleep. For me, wind down starts the when I chose not to look at screens. What you do in that time is entirely up to you but should be relaxing: drink herbal tea, read, journal, shower...
Limit Screen Time: The blue light from phones, tablets, and computers interferes with melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep. Try to avoid screens at least an hour before bed, or use blue light filters if you can’t put them away. I also don't believe in using the blue light filters. I believe they work, but people just use that as as excuse to spend more time on their phone, scrolling, and getting wind up.
3. Watch What You Eat and Drink Before Bed
What you consume in the hours leading up to bedtime can have a big impact on how well you sleep. Certain foods, drinks, and habits can either help or hinder your sleep quality.
Eat at least 2 hours before bed: Eating a large meal right before bed can make it uncomfortable to fall asleep. The reason being your body will be actively digesting the food which takes energy. If you need a pre bed snack, if it's part of your routine, keep it light.
Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Caffeine can stay in your system for up to 10 hours, so it’s best to cut off your coffee intake in the afternoon. While alcohol might make you feel sleepy initially, it can disrupt your sleep cycle and prevent you from getting deep, restorative sleep.
Hydrate Smartly: Stay hydrated throughout the day, but try to limit how much you drink right before bed to avoid those late-night bathroom trips.
4. Use Natural Sleep Aids (When Needed)
Sometimes, even with the best sleep habits, you might need a little extra help getting quality rest. Natural sleep aids can support your body’s ability to fall and stay asleep.
Magnesium: This mineral is known to promote relaxation and calmness, making it a great natural aid for better sleep. You can find magnesium in supplements or through foods like leafy greens, nuts, and seeds. If you are taking the supplement route, magnesium glycinate is the one you want.
Herbal Teas: Drinking a calming tea, like chamomile or valerian root, before bed can help relax your mind and body, making it easier to drift off.
In times of extreme need, you could look at melatonin, but I generally don't recommend using it too much. Supplementing something that your body is supposed to produce on it's own can lead to dependancies which isn't ideal.
5. Exercise and Sleep – Timing Matters
Regular exercise is fantastic for improving sleep quality, but when you work out can make a difference.
Exercise Regularly: Studies show that regular exercise can help you fall asleep faster and improve sleep quality. Just 30 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise, like walking or cycling, can make a noticeable difference. Or my classic 5 min push up challenge pre bed also works.
Avoid Late-Night Workouts: You know what makes a intense workout amazing? Getting hyped! Loud music, intense visualization and lifting heavy weights. Yea buddy!! You know what is very detrimental to falling asleep? Being hyped. I usually need a couple hours to mentally, and physically calm down after an intense workout. Generally speaking try to finish your workouts a couple hours before you plan on going to bed.
Focusing on the quality of your sleep will pay huge dividends with your fitness goals.
Conclusion: Sleep is the Secret Weapon for Your Fitness Success
By now, you’ve probably realized (I hope) that sleep isn’t just a “nice-to-have” part of your health routine, it’s a must have. Whether you’re trying to build muscle, burn fat, or simply feel better overall, sleep plays a crucial role in helping you reach your goals.
Think of sleep as the foundation of your fitness efforts, mainly because of the rest and repair functions. Without it, everything else—workouts, nutrition, motivation—just doesn’t work as well.
Take the time to set up your bedroom in a way that will promote sleep and getting to sleep.
Happy training!
Clem
FAQ
Can I make up for lost sleep on the weekends?
Unfortunately, you can’t completely "catch up" on sleep debt by sleeping in on weekends. While getting extra rest can help you feel more refreshed, the long term effect of irregular sleep times is detrimental.
How does poor sleep affect weight loss?
Poor sleep can seriously hinder weight loss efforts. Sleep deprivation disrupts the hormones that control hunger (ghrelin) and fullness (leptin), making you more likely to overeat or crave unhealthy foods. Additionally, lack of sleep slows your metabolism and increases fat storage, especially around the belly via increased cortisol levels.
Will napping help if I don’t get enough sleep at night?
Napping can be a helpful way to boost energy and recovery, especially if you're not getting enough rest at night. A nice power nap (20-30 minutes) can improve alertness and mood, but it’s important not to rely on those as a replacement for regular, full nights of sleep.
You want to go through all those sleep cycles at night to get the full benefits that sleep produce. Remember that a full sleep cycle can take up to 90 min. We usually don't have that kind of time in our day.
Is it bad to wake up in the middle of the night?
Waking up briefly during the night is normal, but if you're having trouble falling back asleep or waking up multiple times, it could impact your overall sleep quality.
If you find that this is happening regularly, speak with sleep doctor to find the root cause of it and a solution.
What’s the best sleep position for recovery?
The best sleep position is one that allows your body to relax and avoid strain. Sleeping on your back or side is generally considered best for spinal alignment and muscle recovery.





Comments